Leveldb skiplist 实现以及解析
RT
skiplist 原理介绍
skiplist 由William Pugh 在论文Skip Lists: A Probabilistic Alternative to Balanced Trees 中提出的一种数据结构,skiplist 是一种随机化存储的多层线性链表结构,插入,查找,删除的都是对数级别的时间复杂度。skiplist 和平衡树有相同的时间复杂度,但相比平衡树,skip实现起来更简单。
下图是wikipedia 上一个一个高度为4的skiplist
从垂直角度看,skiplist 的第0层以单链表的形式按照从小到大的顺序存储全部数据,越高层的链表的节点数越少,这样的特点实现了skiplist 在定位某个位置时,通过在高层较少的节点中查找就可以确定需要定位的位置处于哪个区间,从高层到低层不断缩小查找区间。以上图为例,比如我们需要在skiplist中查找2,查找过程如下,首先在最高层确定到2只可能处于1->NULL 这个区间,然后在第三层查找确定 2 只可能处于 1->4 这个区间,继续在第二层查找确定2 只可能处于1-3 这区间,最后在最底层1->3 这个区间查找可以确定2 是否存在于skiplist之中。
下图是wikipedia上提供的表示skiplist插入过程的一张gif,此图形象的说明了skiplist 定位以及插入节点的过程。
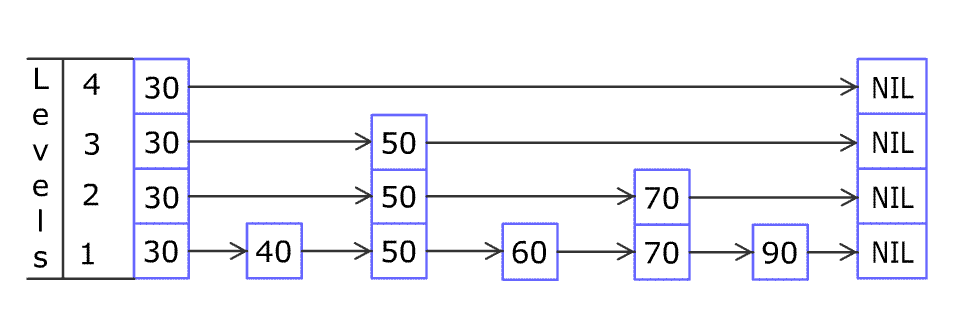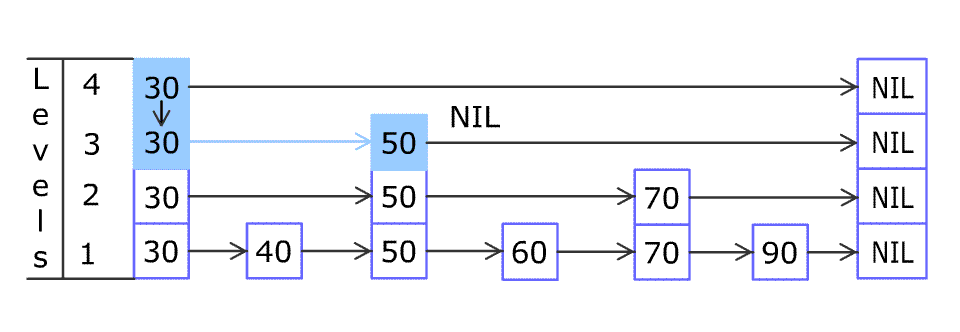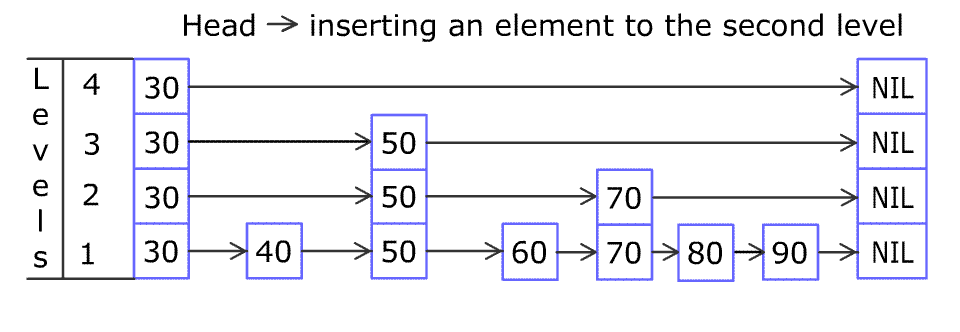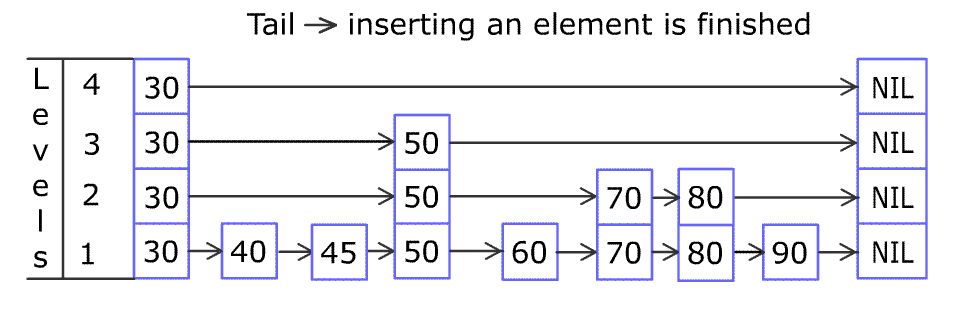
从水平角度来看,skiplist实现在链表开始的时候设置名为head 的哨兵节点,每一层链表的结束为止全部指向NULL。
leveldb 实现
leveldb 实现的skiplist位于db/skiplist.h。
skiplist Node 类型定义
// Implementation details follow
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
struct SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Node {
explicit Node(const Key& k) : key(k) { }
// Node 存储的内容
Key const key;
// Accessors/mutators for links. Wrapped in methods so we can
// add the appropriate barriers as necessary.
// 获取当前节点在指定level的下一个节点
Node* Next(int n) {
assert(n >= 0);
// Use an 'acquire load' so that we observe a fully initialized
// version of the returned Node.
return reinterpret_cast<Node*>(next_[n].Acquire_Load());
}
// 将当前节点在指定level的下一个节点设置为x
void SetNext(int n, Node* x) {
assert(n >= 0);
// Use a 'release store' so that anybody who reads through this
// pointer observes a fully initialized version of the inserted node.
next_[n].Release_Store(x);
}
// 无内存屏障版本set。关于leveldb 内存屏障在新一篇博客介绍
// No-barrier variants that can be safely used in a few locations.
Node* NoBarrier_Next(int n) {
assert(n >= 0);
return reinterpret_cast<Node*>(next_[n].NoBarrier_Load());
}
void NoBarrier_SetNext(int n, Node* x) {
assert(n >= 0);
next_[n].NoBarrier_Store(x);
}
private:
// Array of length equal to the node height. next_[0] is lowest level link.
// 当前节点的下一个节点数组
port::AtomicPointer next_[1];
};
skiplist 类成员变量
private:
// 使用枚举类型定义skiplist 最高高度
enum { kMaxHeight = 12 };
// Immutable after construction
// 用户定制的比较器
Comparator const compare_;
// leveldb 实现的简单的内存分配器
Arena* const arena_; // Arena used for allocations of nodes
// skiplist 的前置哨兵节点
Node* const head_;
// Modified only by Insert(). Read racily by readers, but stale
// values are ok.
// 记录当前skiplist使用的最高高度
port::AtomicPointer max_height_; // Height of the entire list
skiplist 插入
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
void SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Insert(const Key& key) {
// TODO(opt): We can use a barrier-free variant of FindGreaterOrEqual()
// here since Insert() is externally synchronized.
// 声明prev节点,代表插入位置的前一个节点
Node* prev[kMaxHeight];
// 使用FindGreaterOrEqual函数找到第一个大于等于插入key的位置
Node* x = FindGreaterOrEqual(key, prev);
// Our data structure does not allow duplicate insertion
assert(x == NULL || !Equal(key, x->key));
// 使用随机数获取该节点的插入高度
int height = RandomHeight();
if (height > GetMaxHeight()) {
// 大于当前skiplist 最高高度的话,将多出的来的高度的prev 设置为哨兵节点
for (int i = GetMaxHeight(); i < height; i++) {
prev[i] = head_;
}
//fprintf(stderr, "Change height from %d to %d\n", max_height_, height);
// It is ok to mutate max_height_ without any synchronization
// with concurrent readers. A concurrent reader that observes
// the new value of max_height_ will see either the old value of
// new level pointers from head_ (NULL), or a new value set in
// the loop below. In the former case the reader will
// immediately drop to the next level since NULL sorts after all
// keys. In the latter case the reader will use the new node.
// 跟新max_height_ max_height_.NoBarrier_Store(reinterpret_cast<void*>(height));
}
// 创建要插入的节点对象
x = NewNode(key, height);
for (int i = 0; i < height; i++) {
// NoBarrier_SetNext() suffices since we will add a barrier when
// we publish a pointer to "x" in prev[i].
// 首先将x的next 指向prev 的下一个节点
x->NoBarrier_SetNext(i, prev[i]->NoBarrier_Next(i));
// 将prev 指向x
prev[i]->SetNext(i, x);
}
}
skiplist 查找
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
bool SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Contains(const Key& key) const {
// 找到大于等于当前key的第一个node,然后判断node 的key
// 和传入的key 是否相等
Node* x = FindGreaterOrEqual(key, NULL);
if (x != NULL && Equal(key, x->key)) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
FindGreaterOrEqual
函数的作用是找到第一个大于或等于指定的key 的node,以及该node的前一个node
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
typename SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Node* SkipList<Key,Comparator>::FindGreaterOrEqual(const Key& key, Node** prev)
const {
Node* x = head_;
// level 从0 开始编码
int level = GetMaxHeight() - 1;
while (true) {
// 定位到当前level的下一个节点
Node* next = x->Next(level);
// key 没有在当前区间
if (KeyIsAfterNode(key, next)) {
// Keep searching in this list
x = next;
} else {
// key 在当前区间,在低level 继续查找,
// 在查找的同时设置prev 节点
if (prev != NULL) prev[level] = x;
// 在最低level找到相应位置
if (level == 0) {
return next;
} else {
// Switch to next list
level--;
}
}
}
}
RandomHeight
利用随机数实现每次有4分之一的概率增长高度。
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
int SkipList<Key,Comparator>::RandomHeight() {
// Increase height with probability 1 in kBranching
static const unsigned int kBranching = 4;
int height = 1;
while (height < kMaxHeight && ((rnd_.Next() % kBranching) == 0)) {
height++;
}
assert(height > 0);
assert(height <= kMaxHeight);
return height;
}
FindLessThan
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
typename SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Node*
SkipList<Key,Comparator>::FindLessThan(const Key& key) const {
Node* x = head_;
int level = GetMaxHeight() - 1;
while (true) {
assert(x == head_ || compare_(x->key, key) < 0);
\// 在当前level 查找
Node* next = x->Next(level);
// if 分支为true 的时候表示需要查找的位置在当前区间
if (next == NULL || compare_(next->key, key) >= 0) {
// 在最后一层停止查找
if (level == 0) {
return x;
} else {
// Switch to next list
level--;
}
} else {
// 在当前level 就找到了比key 小的节点
x = next;
}
}
}
总结
skiplist最底层单链表有序存储全部元素,利用多层有序链表的结构实现加速索引的功能,处于越高level 节点的链表越稀疏查找速度越快,在不断向下查找的过程中不断缩小查找空间。
总的来说,skiplist 是一种设计巧妙的数据结构,相比红黑树实现简单,插入查找删除的时间复杂度和红黑树一致,但是顺序遍历的时间复杂度优于红黑树。leveldb 的实现可读性高,容易理解。