Json library implemented by boost variant
强大的boost
boost variant 介绍
boost variant 是一个不同union的泛型类,它用于存储和操作不同类型但在使用时存在<相同泛型>的对象。variant 在实现不同类型的泛型的同时,提供对其包含的具体类型的安全访问。
基于此性质,boost variant 可以应用于创建json 这种数据结构,我们把json 中的Object, Array, String, Number, True, False, Null 统一当做同一种variant 类型。需要注意的是,json 中的Object 和 Array 类型是递归的variant 类型,在声明时需要使用 boost::recursive_wrapper 修饰。boost::recursivee_wrapper用于创建包含创建的variant类型的表达式。
在访问varint 类型时,可以使用boost::get
更多关于 boost variant 的介绍见:
https://www.boost.org/doc/libs/1_62_0/doc/html/variant/reference.html
json 数据结构
json 的数据类型实现如下
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: json_type.hpp
> Author: ce39906
> Mail: ce39906@163.com
> Created Time: 2018-07-31 16:25:59
************************************************************************/
#ifndef JSON_TYPE_HPP
#define JSON_TYPE_HPP
#include <boost/variant.hpp>
#include <string>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <vector>
namespace json
{
struct Object;
struct Array;
struct String
{
String() {}
String(const char* value) : value{value} {}
String(std::string value) : value{std::move(value)} {}
std::string value;
};
struct Number
{
Number() {};
Number(const double value) : value{value} {}
double value;
};
struct True
{
};
struct False
{
};
struct Null
{
};
using Value = boost::variant<String,
Number,
boost::recursive_wrapper<Object>,
boost::recursive_wrapper<Array>,
True,
False,
Null>;
struct Object
{
bool isMember(const std::string& key) const
{
return values.count(key) != 0;
}
const Value& at(const std::string& key) const
{
return values.at(key);
}
const Value& operator[](const std::string& key) const
{
return values.at(key);
}
std::unordered_map<std::string, Value> values;
};
struct Array
{
const Value& at(const size_t idx) const
{
return values.at(idx);
}
const Value& operator[](const size_t idx) const
{
return values.at(idx);
}
size_t size() const
{
return values.size();
}
const Value& front() const
{
return values.front();
}
const Value& back() const
{
return values.back();
}
std::vector<Value> values;
};
} // ns json
#endif
json 数据访问
本节只介绍使用boost::get
代码示例如下
namespace access
{
inline const Object& asObject(const Value& value)
{
return boost::get<Object>(value);
}
inline const Array& asArray(const Value& value)
{
return boost::get<Array>(value);
}
inline const String& asString(const Value& value)
{
return boost::get<String>(value);
}
inline const Number& asNumber(const Value& value)
{
return boost::get<Number>(value);
}
inline const True& asTrue(const Value& value)
{
return boost::get<True>(value);
}
inline const False& asFalse(const Value& value)
{
return boost::get<False>(value);
}
inline const Null& asNull(const Value& value)
{
return boost::get<Null>(value);
}
} // ns access
json 序列化
json 序列化利用boost::apply_visitor. boost::apply_visitor需要实现一个visitor 函数对象,函数对象针对不同实际类型实现不同的序列化方式,针对Object以及Array 这两种类型需要递归调用visitor。
示例代码如下
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: json_serialize.hpp
> Author: ce39906
> Mail: ce39906@163.com
> Created Time: 2018-07-31 17:23:19
************************************************************************/
#ifndef JSON_SERIALIZE_HPP
#define JSON_SERIALIZE_HPP
#include "json_type.hpp"
#include "json_util.hpp"
#include <vector>
#include <ostream>
namespace json
{
struct SerializeToOstream : boost::static_visitor<void>
{
explicit SerializeToOstream (std::ostream& out) : out(out) {}
void operator() (const String& string) const
{
out << "\"";
out << string.value;
out << "\"";
}
void operator() (const Number& number) const
{
out << util::cast::to_string_with_percision(number.value);
}
void operator() (const Object& object) const
{
out << "{";
for (auto it = object.values.begin(); it != object.values.end();)
{
out << "\"" << it->first << "\":";
boost::apply_visitor(SerializeToOstream(out), it->second);
if (++it != object.values.end())
{
out << ",";
}
}
out << "}";
}
void operator() (const Array& array) const
{
out << "[";
for (auto it = array.values.cbegin(); it != array.values.cend();)
{
boost::apply_visitor(SerializeToOstream(out), *it);
if (++it != array.values.cend())
{
out << ",";
}
}
out << "]";
}
void operator() (const True&) const
{
out << "ture";
}
void operator() (const False&) const
{
out << "false";
}
void operator() (const Null&) const
{
out << "null";
}
private:
std::ostream& out;
};
struct SerializeToString : boost::static_visitor<void>
{
explicit SerializeToString (std::string& out) : out(out) {}
void operator() (const String& string) const
{
out.push_back('\"');
out.append(string.value);
out.push_back('\"');
}
void operator() (const Number& number) const
{
const std::string number_str = util::cast::to_string_with_percision(number.value);
out.append(std::move(number_str));
}
void operator() (const Object& object) const
{
out.push_back('{');
for (auto it = object.values.begin(); it != object.values.end();)
{
out.push_back('\"');
out.append(it->first);
out.push_back('\"');
out.push_back(':');
boost::apply_visitor(SerializeToString(out), it->second);
if (++it != object.values.end())
{
out.push_back(',');
}
}
out.push_back('}');
}
void operator() (const Array& array) const
{
out.push_back('[');
for (auto it = array.values.cbegin(); it != array.values.cend();)
{
boost::apply_visitor(SerializeToString(out), *it);
if (++it != array.values.cend())
{
out.push_back(',');
}
}
out.push_back(']');
}
void operator() (const True&) const
{
out.append("true");
}
void operator() (const False&) const
{
out.append("false");
}
void operator() (const Null&) const
{
out.append("null");
}
private:
std::string& out;
};
void serialize(std::ostream& out, const Object& object)
{
Value value = object;
boost::apply_visitor(SerializeToOstream(out), value);
}
void serialize(std::string& out, const Object& object)
{
Value value = object;
boost::apply_visitor(SerializeToString(out), value);
}
} // ns json
#endif
构造json 结构
针对String,Number,True,False,Null 这类简单类型可以直接使用构造函数构造。
Array 类型内部使用vector 类型,构造时使用vector 的 push_back, emplace_back 方法增加Array的元素。
Object 类型内部使用unordered_map 类型,构造时可以使用 unordered_map 的内建方法。
示例代码如下:
Object obj;
obj.values["string"] = "v1";
obj.values["bool"] = True();
obj.values["null"] = Null();
obj.values["number"] = Number(9);
Array arr;
arr.values.emplace_back(Number(1.02));
arr.values.emplace_back(Number(2.2));
arr.values.emplace_back(Number(3));
arr.values.emplace_back(True());
arr.values.emplace_back(False());
obj.values["array"] = std::move(arr);
示例
示例代码测试构建json对象,访问json对象,以及序列化json 对象。
示例代码如下
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: test_json.cpp
> Author: ce39906
> Mail: ce39906@163.com
> Created Time: 2018-07-31 19:26:17
************************************************************************/
#include <iostream>
#include "json.hpp"
using namespace json;
int main()
{
Object obj;
obj.values["string"] = "v1";
obj.values["bool"] = True();
obj.values["null"] = Null();
obj.values["number"] = Number(9);
Array arr;
arr.values.emplace_back(Number(1.02));
arr.values.emplace_back(Number(2.2));
arr.values.emplace_back(Number(3));
arr.values.emplace_back(True());
arr.values.emplace_back(False());
obj.values["array"] = std::move(arr);
// json access
std::cout << "Test json access.\n";
const auto& arr1 = access::asArray(obj["array"]);
std::cout << "first number in arr is "
<< access::asNumber(arr1.front()).value << std::endl;
// json serialize to ostream
std::cout << "Test serialize to ostream.\n";
serialize(std::cout, obj);
std::cout << std::endl;
// json serialize to string
std::cout << "Test serialize to string.\n";
std::string str;
serialize(str, obj);
std::cout << str << std::endl;
return 0;
}
编译
g++ --std=c++11 test_json.cpp -o test_json
执行
执行结果如下
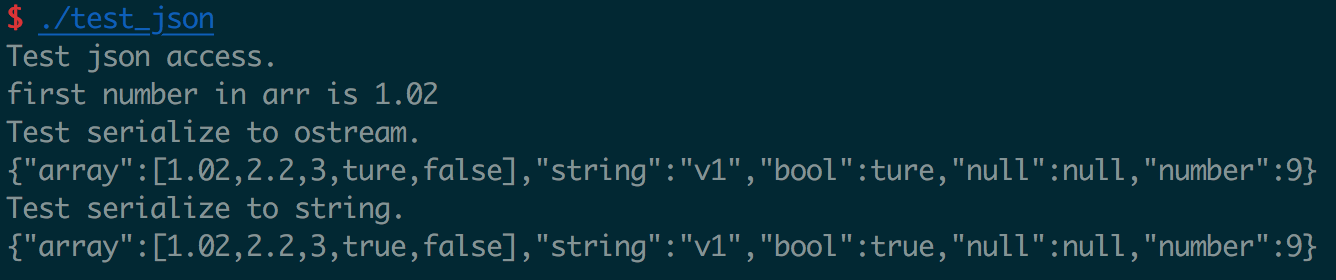
TODO
使用boost spirit 实现json反序列化
完整代码
https://github.com/ce39906/self-practices/tree/master/cppcode/variant_json